Infections of the Spine Treatment
A Cause of Pain, Fevers and Changes in Neurological Function
Osteomyelitis, discitis, epidural abscess and meningitis all represent infections of the spine. Each refers to an infection of a different portion of the spine.
• Osteomyelitis: refers to an infection of the vertebral body itself.
• Discitis: indicates an infection in the disc space.
• Epidural abscess: is an infection or abscess which is present surrounding the dura (covering of the nerves or spinal cord).
• Meningitis: refers to an infection of the spinal fluid which surrounds the spinal cord,
nerve roots, and brain.
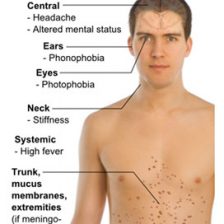
All of these conditions may cause pain, fevers, and changes in neurological function depending upon whether the spinal cord or nerves are compressed or infected.
These infections are typically caused by bacteria, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common. Other types of bacteria or tuberculosis may be responsible as well.
Laboratory studies of the blood, as well as imaging studies of the spine, are essential. White blood cell counts are often elevated. Blood cultures may grow the offending organism. Plain x-rays may show lytic lesions and changes in the bone suggestive of osteomyelitis. MRI scanning will show osteomyelitis, diskitis, and epidural abscess. A spinal tap will show the diagnosis of meningitis. There will be an increase in white blood cells in the spinal fluid, as well as possible bacteria seen under the microscope on Gram stain and bacteria grown in culture.
Conditions that increase one’s risk of developing these infections include diabetes, intravenous drug abuse, chronic renal failure, alcoholism, cancer, recurrent urinary tract infections and the presence of HIV. Long-term steroid use, as well as spinal operations, trauma or gunshot wounds to the spine also predispose to these infections.
All of these types of infections will require the diagnosis of which organism is causing the infection. A significant epidural abscess may need surgery to remove a portion of the lamina and drain the abscess. Discitis and osteomyelitis may be treated with antibiotics. Meningitis may be treated with antibiotics.
The prognosis will depend on the severity of the infection and how much neurological damage has been caused. If paralysis has been caused by an epidural abscess, depending on how quickly the abscess is removed, recovery from paralysis varies. Osteomyelitis, diskitis, and meningitis may be well treated with appropriate antibiotics.